What are the United States and the European Union doing against the economic crisis? Reference report
In the US, fiscal policy has been more extensive: “Fiscal drivers” show a stimulus to the economy at 5-6% of GDP in the US and around 3 points in the Eurozone. Analysis of economist Fedele De Novellis, president of Congiuntura ref
The possibility of limiting the spread of the epidemic opens the prospects for the gradual removal of restrictions on behavior, with positive effects on the performance of US economic activity. In fact, all current outlook scenarios omit the recovery phase at a relatively fast pace once restrictions are eased.
The second quarter in the US is likely to already be marked by a strong acceleration in GDP, while in the euro area the reversal is postponed to the third quarter provided the expected acceleration in the vaccination campaign occurs. This means that the Eurozone economic cycle could remain out of stage with the American session. In this regard, the latest economic indicators confirm a recovery in manufacturing in the US as well as in the Eurozone.
This is the trend that characterizes the entire global economy as a result of the gradual removal of restrictions on the purchase of goods after the first closure, followed by the phase of renewal of warehouses, which were greatly reduced in size in that period.
In some cases, this trend is underlined by a reorientation of global demand from services to goods, such as in the case of consumer electronics or furniture.
On the other hand, it is the data for the spring months that should set the economic scenario apart after a more pronounced recovery in the US. Indeed, as the divergence measures decrease, growth will be more vibrant, especially in the service sectors.
Among the factors that lead us to believe that another gap in US growth will be observed compared to the Eurozone, there is also a different approach to budgetary policies.
In 2020, the crisis affected the public budgets of all countries through a direct impact on the balances, mainly due to lower revenues, and following the measures taken by governments to support the economy.
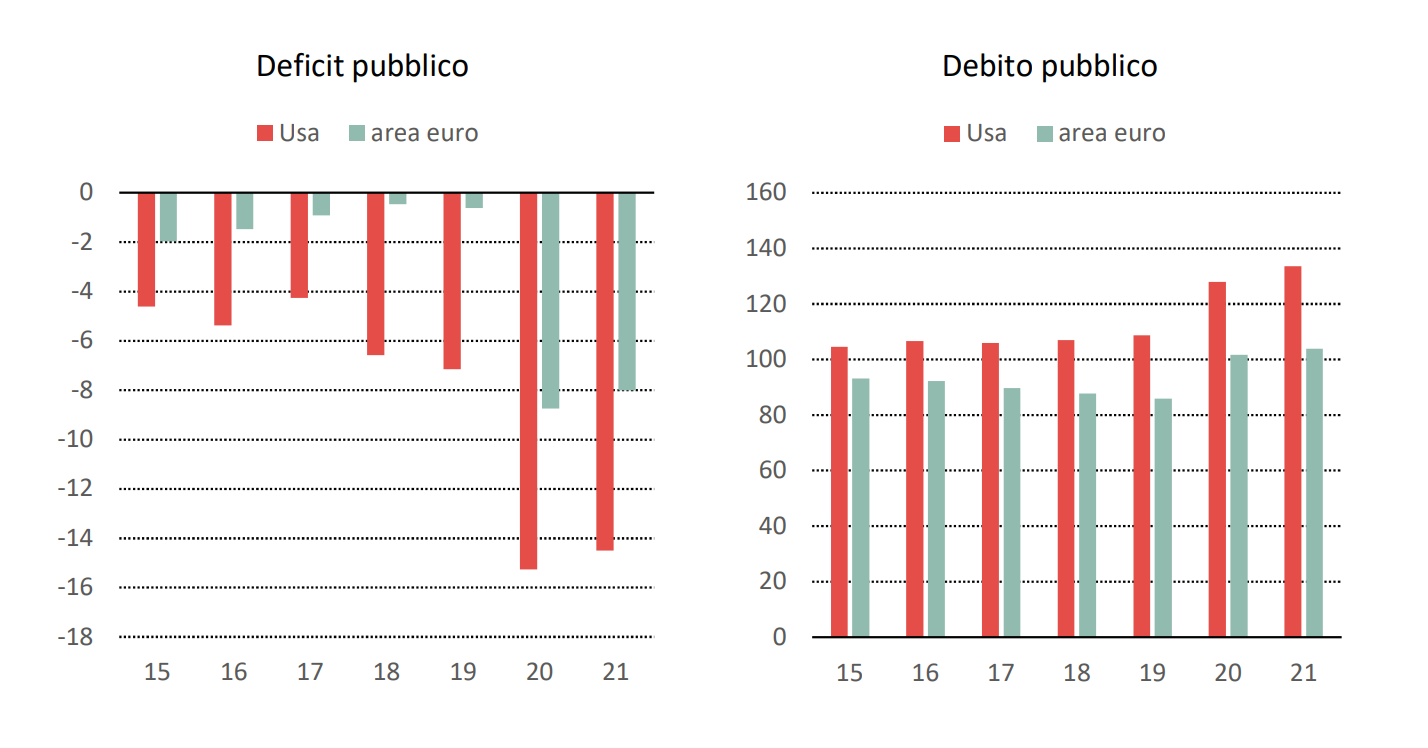
However, the subsequent quantification of fiscal measures adopted in various countries shows that the fiscal policy of the United States has been more expansionary: “fiscal drivers”, calculated on the basis of changes in the structural primary balance, show a stimulus to an economy of 5-6 percent of GDP. In the United States and about 3 points in the euro area.
Before the outbreak of the crisis, the United States was already running a much higher deficit than the eurozone (in 2019 the US general deficit was 6.7 percent of GDP, compared to the near-balance in the eurozone).
Consequently, the increase in 2020 pushed the US deficit to 15 percent of GDP, compared to roughly 8.5 percent in the euro area.
Many of the measures adopted by governments in the past year are transitional in nature; That is, they tend to have a finite duration of time. For this reason, it is likely that during 2021 governments will have to take measures to refinance this type of intervention (as happened for example in Italy with Supports Dl). In fact, the prevailing approach in the eurozone is to “follow the economic cycle,” or refinance this type of measure until the epidemic is over. Therefore, with vaccination campaigns at an advanced stage, public budgets must improve greatly, and benefit from the effects of the recovery and the failure to renew support measures.
It is understood that in such a framework, the fiscal balances for 2022 will be better, the stronger the recovery we will notice in the coming quarters. However, in recent months, a different approach has emerged between the United States and the eurozone with regard to budgetary policies. In the US, budget policy aims to provide an expanded boost this year despite significant advances in vaccination campaigns, which have improved the economic outlook.
In particular, if at the end of 2020 in the United States of America a package of measures had already been launched with a total amount of $ 900 billion (Response and Relief Act), equivalent to more than 4 percent of GDP, by the previous administration, the incentives Adopted by Biden (the US bailout), it is equal to 1900 billion, or 9 percent of the gross domestic product of the United States, of which more than 6 are in effect until 2021.
The result is that the US deficit will again reach about 15 per cent of GDP this year. In the eurozone, as we have seen, new tax packages will likely be launched in the coming months by various countries, but in any case we will not go beyond 2020 levels.
For this reason, the distance between the United States and the Eurozone in public deficit levels will remain large. Starting from these levels of public deficit, it will also result that the ratio between public debt and GDP for the eurozone as a whole will continue to increase this year, reaching 104 percent of GDP, while in the United States the ratio will approach 135 percent of gross domestic product.

Communicator. Reader. Hipster-friendly introvert. General zombie specialist. Tv trailblazer






