Virus resurgence dragging on eurozone recovery, details counsel

Europe is established for an economic rebound in the third quarter, but substantial-frequency data indicators stage to slowing momentum in nations which have observed a resurgence of cases of the virus — particularly Spain.
This has prompted economists to alert that the recovery might be slower than earlier assumed.
The eurozone overall economy will improve by 8.6 for each cent in the third quarter, according to the consultancy Oxford Economics. That would be the swiftest pace since information commenced in 1995, but it would only partly claw back the report drop in output in the second quarter.
The coronavirus pandemic plunged the eurozone into a historic economic downturn, with gross domestic solution falling by 12.1 per cent quarter on quarter in the second quarter of 2020, following a decline of 3.6 for every cent in the initial 3 months of the calendar year.
There was an initial rebound in June and the tempo of the restoration depends on activity continuing to strengthen, but economists warn that the craze is threatened by the resurgence of bacterial infections in various sections of the bloc.
Sentiment indicators this kind of as shopper and company surveys and different economic info, these kinds of as mobility and cafe bookings, present that the recovery continued in July and August, but they also propose that action is losing momentum in some nations around the world.
Each styles of steps are much less complete and trusted than official data, but they have grow to be broadly viewed due to the fact the pandemic as they supply a far more well timed gauge of the financial system.
Different indicators are also now a lot more difficult to interpret as the modifications in output are much less extraordinary than through lockdown and they fall short to account for seasonal effects.
“The important examination of the V-shaped restoration thesis is most likely to arrive with the restart of universities, and no matter if that helps drive . . . [activity levels] larger, or as an alternative effects in additional community lockdowns being introduced and exercise rolling about,” stated Marchel Alexandrovich, economist at the financial investment bank Jefferies.
Spain
The epicentre of Europe’s recession is Spain, which has observed the major surge in new bacterial infections.
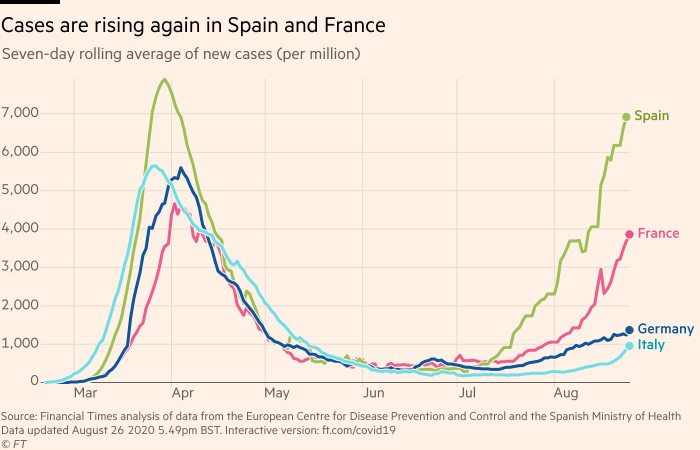
Sentiment indicators and superior-frequency details recommend that it is progressively owning an outcome on the country’s economy.
The variety of outings to transportation hubs, such as airports, train and bus stations, has declined in latest weeks, according to cell cellphone destinations tracked by Google. Outings to retail and amusement venues, dining places and bars also edged down 7 days on week in mid-August.
Box business office receipts also give evidence of a refreshing slowdown. After an initial put up-lockdown rebound they fell sharply in the third weekend of August.
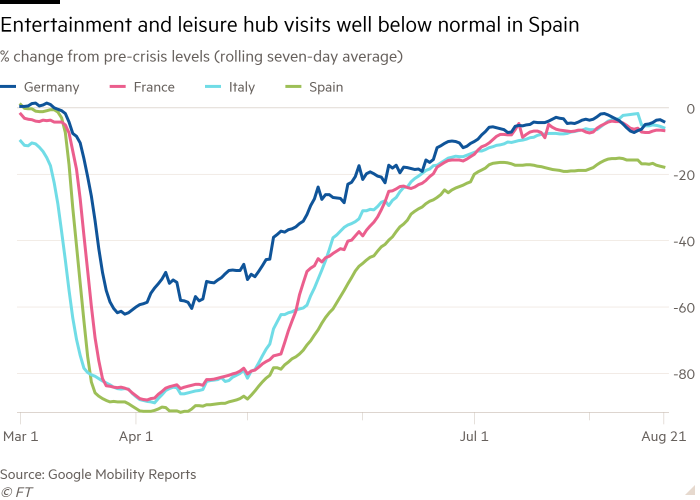
Generally this is the large period for Spain, when huge inflows of worldwide tourists fuel a soar in customer shelling out. Past calendar year turnover in foods and beverage expert services was a single-3rd greater in July and August than in the initial two months of the calendar year.
But the overseas people are mainly lacking this yr.
Claus Vistesen, chief eurozone economist at the consultancy Pantheon Macroeconomics, mentioned that the Spanish financial system came into the Covid-19 crisis as the euro’s star performer, but it is now at “the base of the pile”.
Spanish data “are beginning to show signals of rolling more than, indicating that the jump in new conditions, and connected limitations, are commencing to get their toll”, he mentioned.
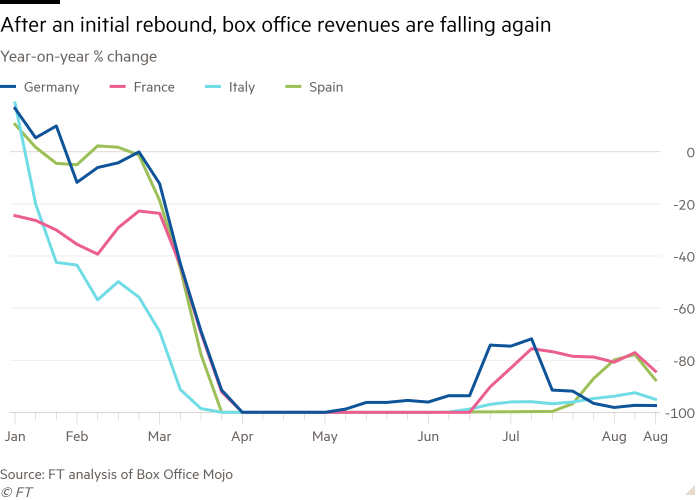
Nicola Nobile, economist at Oxford Economics, mentioned the current limits launched in Spain in a bid to gradual the distribute of the virus had brought on her organisation to revise downwards its forecast of Spanish 3rd-quarter GDP.
“While we are not nevertheless committed to downward revisions in forecasts for other countries, the modern rise in infections has elevated that chance,” she warned.
France
While organization sentiment and substitute indicators recommend that economic action is proving more resilient so considerably in France irrespective of an upsurge in new virus infections, other indicators advise that the restoration may be fragile.
Residence sentiment and mobility facts propose that action was largely unchanged thirty day period on month in August, despite the fact that box office revenues dipped.
Jessica Hinds, Europe economist at Capital Economics, explained the French restoration was probable to outpace that of Spain as the place is considerably less reliant on tourism, has a much larger IT and finance sector in which remote doing the job is far more popular and has benefited from more generous authorities support.
Still she warned that there was a hazard that the French overall economy could plateau very well underneath its amount before the pandemic strike.
“France’s street again to pre-disaster levels will be protracted, and output is however set to be under its pre-virus stage by the finish of 2022,” she reported.
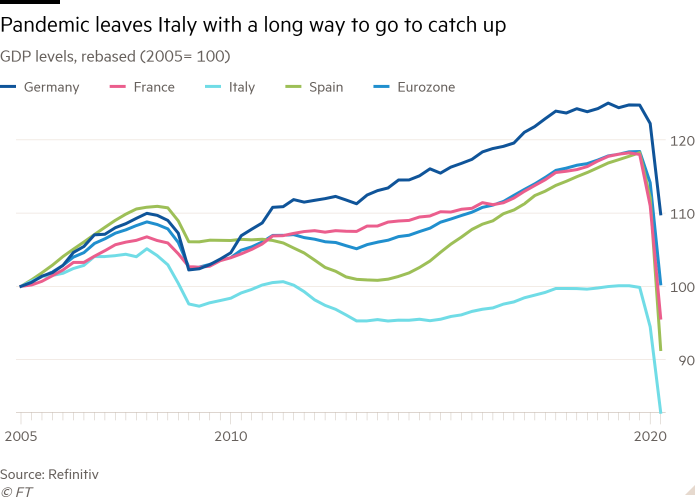
Italy and Germany
Italy and Germany have registered much smaller figures of new bacterial infections than France and Spain and alternate information and sentiment indicators held steady or improved in August.
But, in several other respects, their knowledge of financial recovery differs.
German output has fallen much less seriously than in other major economies — down 11.5 per cent in the second quarter when compared to the end of 2019, compared to minus 17 for Italy and minus 18.9 for France — and in lots of places exercise has returned to normal ranges.
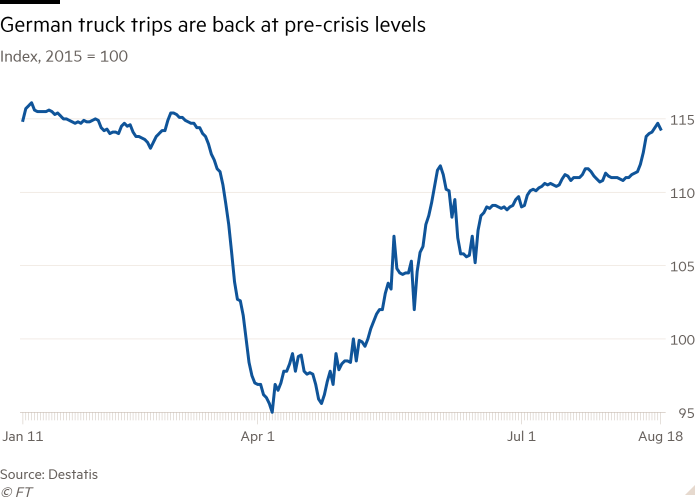
As of late August, Germany’s truck toll mileage index, a proxy for industrial production, was again to pre-disaster levels and German cafe bookings have been up on previous year’s.
“Germany seems to be the most superior in terms of experimental exercise facts,” claimed Carsten Brzeski, chief economist for the eurozone at ING Investigate.
But Italy requires to rebound from a much greater drop that has wiped out extra than two many years of growth and pushed up its presently-substantial public financial debt.
So the north-south divide which plagued the European financial system even prior to the pandemic strike appears to be set to be exacerbated by a two-speed recovery, economists alert.
“Recovery immediately after the original rebound will be much much more uneven,” stated Mr Brzeski. “It will take right up until future 12 months, with the European Recovery Fund kicking in, right before the gap between north and south need to be narrowed.”

Communicator. Reader. Hipster-friendly introvert. General zombie specialist. Tv trailblazer






