How NASA is dealing with the ‘dent’ in Earth’s magnetic field
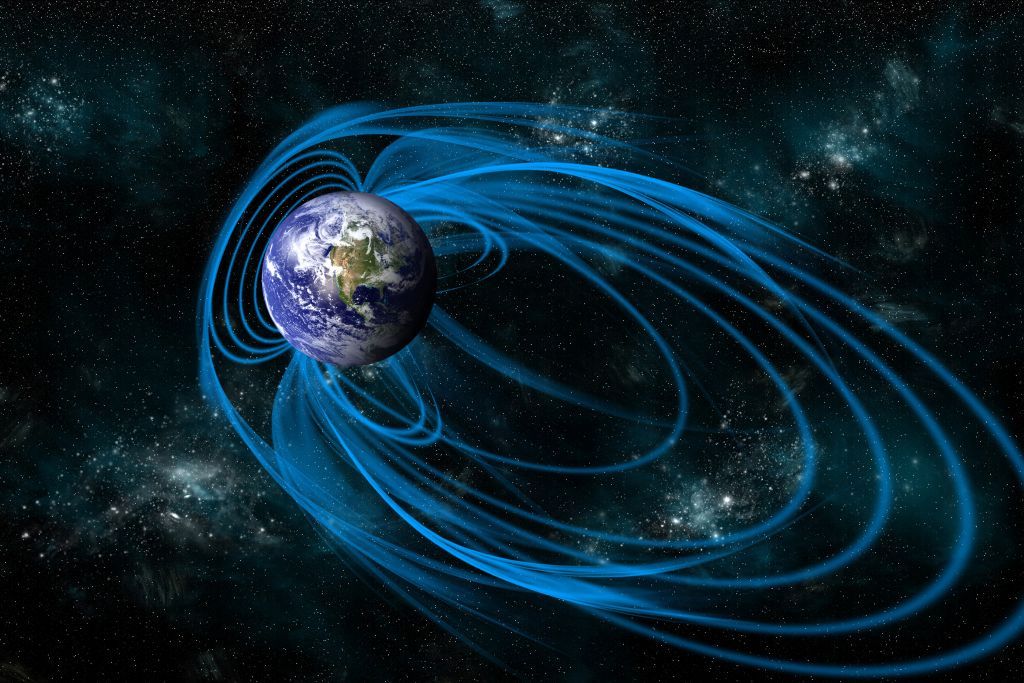
Earth is an great magnet, its iron-wealthy main building a defend of magnetic industry that envelopes the earth —— nicely, almost. A “dent” in this magnetic discipline regarded as the South Atlantic Anomaly will allow billed particles from the sun to dip nearer to the world in an place around South The us and the Southern Atlantic Ocean.
These particles, at the extremely minimum, can mess with devices up in space. So NASA scientists and other scientists have no alternative but to adapt to this hiccup in the magnetic area, switching off satellite devices that move by the SAA and accepting the reduction of some facts on devices aboard the Global House Station (ISS). They’re also preserving close tabs on the SAA, according to a new report from NASA’s Goddard Room Flight Centre.
Similar: What if Earth’s magnetic discipline disappeared?
“Even although the SAA is sluggish-shifting, it is heading by way of some change in morphology, so it truly is also critical that we maintain observing it,” Terry Sabaka, a geophysicist at Goddard in Maryland, reported in the piece.
The anomaly
Earth’s magnetic field is the products of its iron-wealthy outer core, which produces the area as it swirls all over the internal main. The area guards Earth’s environment from staying slowly but surely stripped absent by charged particles from the sunlight. It also protects electronic products on Earth from this similar bombardment.
Commonly, particles from the solar are either deflected by the discipline or turn out to be trapped in two zones called the Van Allen Belts, which let the particles no closer than about 400 miles (644 kilometers) from Earth’s surface. This provides plenty of space to safeguard the earth and its human-introduced satellites. The ISS, for instance, orbits about 220 miles (350 km) higher than the Earth’s floor.
But the magnetic industry is weakening, creating some experts imagine it may well be about to reverse, swapping its north and south poles. (Alternatively, it might go as a result of a weak stage and then improve again, as has transpired in the previous.) Ground zero for this weakening appears to be the South Atlantic Anomaly, an odd spot of unique weakness that stretches concerning South The us and Africa. The zone is switching, with modern study suggesting that it is acquiring not 1, but two, separate minimal factors.
Related: 7 methods Earth alterations in the blink of an eye
Now, satellites that pass via the SAA should do so with numerous delicate instruments turned off, according to Goddard. When the ISS passes by it, some of the space station’s instruments are susceptible to “blips” triggered by the larger exposure to photo voltaic particles. The Worldwide Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) mission, for illustration, encounters a electrical power reset about when a thirty day period and loses a few hrs of knowledge each individual time many thanks to the SAA.
Fortunately, “these functions cause no damage to GEDI,” Bryan Blair, the mission’s deputy principal investigator and a lidar instrument scientist at Goddard, claimed in the agency’s posting.
Tracking the improvements
Goddard experts and their colleagues close to the globe are keeping tabs on the SAA, both equally to make guaranteed their functions are shielded from its effects and to try out to understand how the anomaly will alter in the upcoming.
Utilizing facts from SAMPEX (the Photo voltaic Anomalous and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer), a satellite that released in 1992 and collected details until 2012, Goddard researchers learned that the SAA is drifting a little bit westward, success posted in the journal Place Weather conditions in 2016. The European Room Company (ESA) introduced a established of satellites regarded as Swarm in 2013 that give detailed observations of the Earth’s magnetic area and modifications in the SAA. It was info from Swarm satellites that showed the development of two individual minimum amount-toughness details in the SAA, hinting that the anomaly may break up into two different zones.
Examining this info lets satellite engineers to style their satellites to withstand the amount of solar radiation that they’ll probable come upon once in orbit, according to Goddard. Researchers are also combining the observational facts with versions of Earth’s core dynamics to try out to forecast what the anomaly will do subsequent.
“This is comparable to how weather forecasts are generated, but we are operating with much extended time scales,” Andrew Tangborn, a mathematician in Goddard’s Planetary Geodynamics Laboratory, said in the Goddard report.
In the meantime, researchers outside the house of NASA are doing work to recognize the back links concerning the movement of the outer main and the attributes of the magnetic field it produces. Scientists from the University of Liverpool in England not too long ago reported that volcanic rocks produced from lava that erupted long ago on the Atlantic island of Saint Helena exhibit magnetic anomalies relationship again to in between 8 million and 11.5 million a long time in the past, suggesting that this area of the South Atlantic Anomaly has been unstable for thousands and thousands of years.
At first printed on Stay Science.

Communicator. Reader. Hipster-friendly introvert. General zombie specialist. Tv trailblazer





